Complexation
Définition: Association (M-L)
M et L non identifiés par des réactions caractéristiques. Leurs propriétés analytiques sont dissimulées.
Donneur de particule
(1) 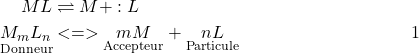
- Mononucléaire
- Polynucléaire
- Ligands = Coordinats
- Indice de coordinance: L M
- Structure (gaz inertes)
Différents types de Complèxes
- Simples : ex:
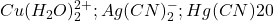
- Chélates : ex:
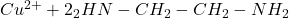 (éthylène diamine, ac. Aminés (zwitterionique+-), dipyridine
(éthylène diamine, ac. Aminés (zwitterionique+-), dipyridine 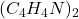
Autres chélateurs:
- Hydroxy8quinoléine (Mg du Sang; Al de l’eau pour hémodialyse)
- Diméthylglyoxine (Ni)
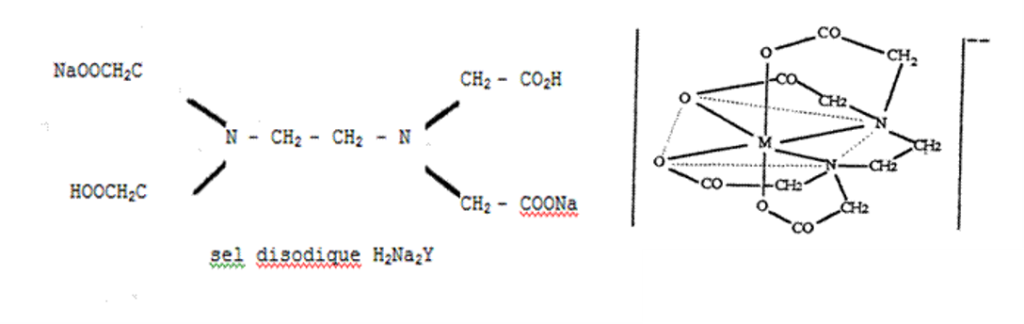
- EDTA (Ca, Mg, Fe…)
- Glyoxal (Ca); Thiourée (Bi); Phénanthroline (
 ); Indicateurs (NET…)
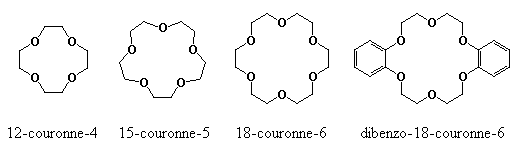
); Indicateurs (NET…) - Éther couronne (piégeage sélectif des ions légers) (Voir Pharmacopée)
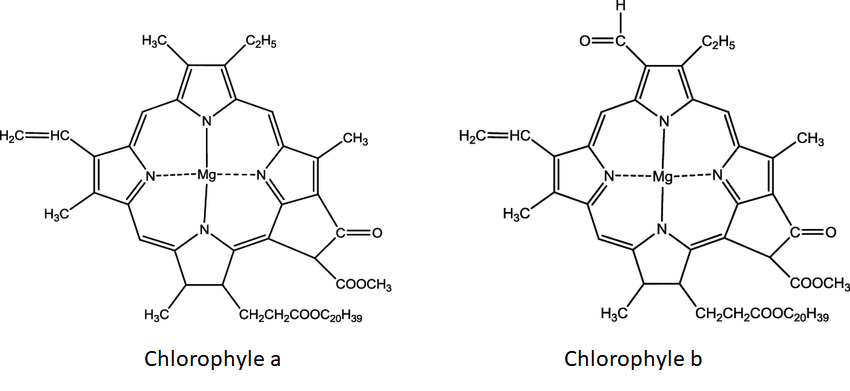
NB: Chélates naturels: Chlorophylles ( ![]() ); hémoglobines (
); hémoglobines ( ![]() )
)
Ex. de formation de Complexes:
Complexe M- EDTA :
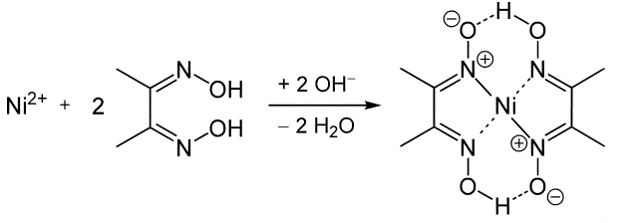
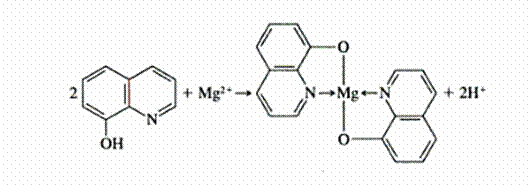
Éthers couronnes : Li, Na, K :
Chlorophylles : sont constituées d’un noyau tétrapyrrolique avec un magnésium en son centre, et estérifié avec un alcool à très longue chaine en C20 (le phytol).
Aspects qualitatifs
- Complexe parfait : pas de dissociation ex:
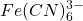 = (Ferricyanure) ,
= (Ferricyanure) , 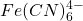 = (Ferrocyanure)
= (Ferrocyanure) - Complexe imparfait : dissociation partielle. ex:
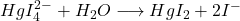
Aspects quantitatifs: (constante de stabilité)
un complexe est toujours partiellement dissocié:
- Constante de stabilité
- Constante de dissociation:
Exemple:
(2) 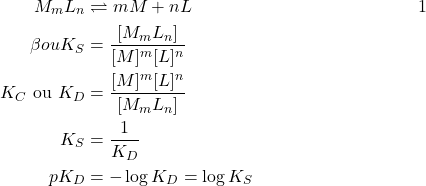
K évalue la force des complexes
- Plus
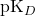 grand: plus l’accepteur est fort donc le complexe est stable.
grand: plus l’accepteur est fort donc le complexe est stable. - Plus
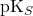 petit: plus le complexe est stable.
petit: plus le complexe est stable.
Complexes successifs
(3) ![]()
Si n supérieur à 1, addition successive de L:
(4) 
(5) ![]()
(6) 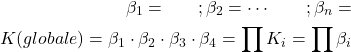
(7) 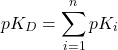
Réactions secondaires
exemple:
(8) ![]()
On acidifie:
(9) ![]()
- Réactions secondaires au niveau de M:
- OH ML; ML2…..
- M
- L MOH; M(OH)2 …..
- Réactions secondaires au niveau de L:
- H ML; ML2 ……
- L
- M HL; H2L …..
Remarque:
(10) 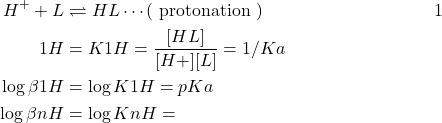
Ex:
(11) ![]()
Dissociation des Complexes; notion de pL
prévision des réactions:
(12) 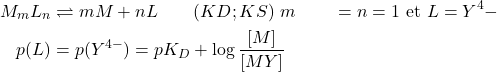
Échelle de pKd
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
\begin{table} ntering \begin{tabular}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}} & {Li^+} & & $pK_D = 2,8$ \\ &{MgY^{2-}} & { Mg^{2+}}& & $pK_D = 8,7$\\ & {ZnY^{2-}} & {Zn^{2+}}& & $pK_D = 16,3$ \\ &{FeY^-} & {Fe^{3+}}& Accepteur Fort & $pK_D = 25,1$\\ \end{tabular} \end{table}
*** Error message:
Not in outer par mode.
leading text: $ \begin{table} n
Undefined control sequence \@currbox.
leading text: $ \begin{table} n
Missing number, treated as zero.
leading text: $ \begin{table} n
Missing $ inserted.
leading text: ...tabular}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...ular}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...lar}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}}
Missing } inserted.
leading text: ...}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}} &
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}} &
Missing } inserted.
leading text: ...}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}} &
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...}{lllll} Donneur Fort & {{LiY^3-}} &
Ex:
(13) 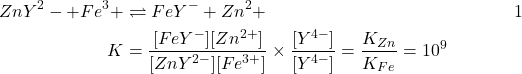
[FeY- pKD-2 pKD pKD+2 Fe3+ p(Y4-)
Déplacement de M1L peu stable par M2 pour former ![]() très stable
très stable
Influence de la concentration sur Kd:(ML; ![]() et
et ![]() )
)
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
\begin{table} ntering \begin{tabular}{ccccc} ML& $\rightleftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}& & - & & - \\ ${C_0}(1-\alpha )$& & $\alpha C_0$ & & $\alpha C_0$ \\ \end{tabular} \end{table}
*** Error message:
Not in outer par mode.
leading text: $ \begin{table} n
Undefined control sequence \@currbox.
leading text: $ \begin{table} n
Missing number, treated as zero.
leading text: $ \begin{table} n
Missing $ inserted.
leading text: ...tleftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...eftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}
Missing } inserted.
leading text: ...ftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}&
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...ftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}&
Missing } inserted.
leading text: ...ftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}&
Extra }, or forgotten $.
leading text: ...ftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}&
Missing } inserted.
leading text: ...ftharpoons$ & M & + & L \\ {C_0}&
![]()
- Plus
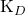 grand, plus
grand, plus 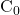 petit plus le complexe se dissocié.
petit plus le complexe se dissocié. - Un excès de L favorise la formation de ML
Relation entre structure et stabilité
Ion coordinateur
Petite dimension; sym. et charge élevée;
Faible électronégativité.
Ligand
- Minéraux : pas de règle générale (pouvoir donneur)
- Chélates:
- Rapport (L/M) ex:
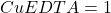 et
et 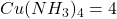 ;
;
- Nombre de cycles;
- Nombre d’atomes du cycle (hexa.,penta.);
- Nature des atomes donneur (N, O et S, P, As)
- Rapport (L/M) ex:
NB: Complexation: essais limites , (détermination des métaux lourds)
Share this content:
Table des matières